6 The cardiovascular system
Figure 50: An overview of the CVS from About the circulatory system (American Heart Association).
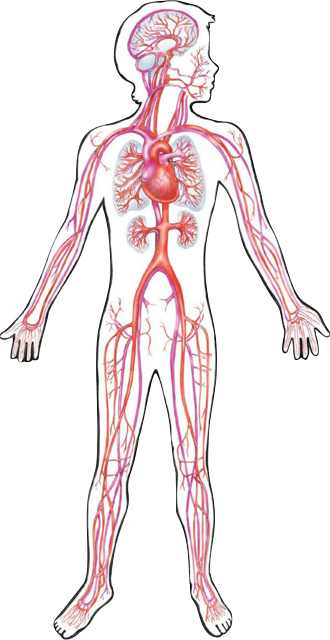
The cardiovascular system has three main components. a) Blood is the medium of convective transport of oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutritients, and other solutes between the organs, followed by diffusive transport to the tissues at cellular level. Without this convective transport an appropriate exchange of the solutes would be impossible due to a too large diffusional resistance [3]. b) The circulatory system is the distribution system for blood and is made up of a network of blood vessels, namely the arteries which transport blood away from the heart and the veins, which the veins which transport towards the heart. c) The heart is a four-chambered pump that drives the blood flow in the circulatory system. The circulatory system may be subdivided into two systems in series, the pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation (Figure 50). Blood flows from the superior and inferior vena cava in to the right atrium, then through the tricuspid valve in to the right ventricle, subsequently through the semilunar valves into the pulmonary artery, which strongly bifurcates in pulmonary arterioles transporting the blood to the lungs. Oxygenated blood is the transported through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium, and further through the mitral valve, the left ventricle, and finally thorough the aortic valve into the aorta. The peripheral circulation starts with the aorta, perfuses various organs, and returns to the right atrium. In each organ, flow begins in the arteries, perfuses the micro-circulatory bed, and finally drains into veins. The vena cava drain blood from the various organs, and return it to the heart [4].