 Introducing the DSC Cooling Accessories
Introducing the DSC Cooling Accessories Introducing the DSC Cooling Accessories
Introducing the DSC Cooling Accessories
The DSC operates in conjunction with one of the cooling accessories listed below. Selection of a cooling accessory is generally based on the temperature range that will be used in subsequent experiments. Ease-of-use is also a factor. The Refrigerated Cooling System (RCS), because it is a self-contained unit requiring no addition of external coolant, is recommended for most applications.
Select from the following topics for more information:










The Finned Air Cooling System (shown to the left), also called the finned cooler, allows operation from ambient to 725°C, using flowing air as the coolant. An optional quench cool accessory can be used with the FACS for faster return to ambient.
This accessory (shown to the right) is placed inside the FACS and has a reservoir into which you can place coolant to return the cell to ambient more quickly. The rate of temperature drop depends on the coolant used (ice and water, dry ice, or liquid nitrogen).
NOTE: When using the FACS quench cool accessory make sure that the Cooler Selection identified on the Tools/Instrument Preferences/DSC Page is the FACS and not the Quench Cooler. If the wrong cooler is identified your results will be inaccurate.
Click here for installation instructions  more.
more.
 The Refrigerated Cooling Systems (RCS) are used to perform
DSC cooling experiments. Both models have a cooling head, which is made
up of an internal heat exchanger, anti-condensate heaters, and various
other components. The cooling head fits over the DSC cell. The
RCS coolers are not compatibile with the Q20P or Q10P or the DSC pressure
cell. Two different models are available:
The Refrigerated Cooling Systems (RCS) are used to perform
DSC cooling experiments. Both models have a cooling head, which is made
up of an internal heat exchanger, anti-condensate heaters, and various
other components. The cooling head fits over the DSC cell. The
RCS coolers are not compatibile with the Q20P or Q10P or the DSC pressure
cell. Two different models are available:
RCS90 with an operating range of -90°C to 550°C.
RCS40 with an operating range of -40°C to 400°C. (The RCS40 is compatible with the DSC Q2000, Q200, and Q20 only.)
The RCS attaches to the cell via a remote cooling head, which remains in place whether you are conducting programmed heating, cooling, cyclic, or Modulated DSC experiments. See also: About the RCS
CAUTION: We recommend that you do not use the RCS when running isothermal experiments above 400°C. Damage to the unit can occur if used at high temperatures for extended periods.
 The Quench Cooling Accessory (QCA) is designed for rapidly
cooling the DSC cell to a lower temperature before initiating programmed
heating experiments. The DSC QCA fits over the standard DSC cell and has
a reservoir into which you can place coolant to cool the cell. The temperature
when using the QCA is –180 to 550°C. The actual range depends on the coolant
(ice and water, dry ice, or liquid nitrogen).
The Quench Cooling Accessory (QCA) is designed for rapidly
cooling the DSC cell to a lower temperature before initiating programmed
heating experiments. The DSC QCA fits over the standard DSC cell and has
a reservoir into which you can place coolant to cool the cell. The temperature
when using the QCA is –180 to 550°C. The actual range depends on the coolant
(ice and water, dry ice, or liquid nitrogen).
Before you initiate a heating experiment, you will need to remove the QCA and put the enclosure lid back in place. See also: About the Quench Cooling Accessory
NOTE: The QCA cannot be used to perform a Tzero calibration of the DSC. Therefore, only T1 heat flow is available when using the QCA.
NOTE: The QCA requires manual lids and therefore cannot be used with the Autosampler. The AutoLid is deactivated ("parked") during quench cooling operation.
Click here for installation instructions  more.
more.
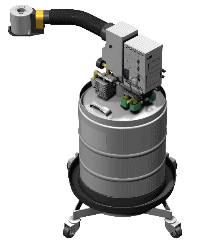 The LNCS (Liquid
Nitrogen Cooling System) is a universal cooling accessory for use with
TA Instruments Analyzers.
The LNCS (Liquid
Nitrogen Cooling System) is a universal cooling accessory for use with
TA Instruments Analyzers.
The Liquid Nitrogen Cooling System (LNCS) allows automatic and continuous temperature control within the range of –180°C to 550°C. The LNCS tank is pressurized to deliver the liquid nitrogen to the heat exchanger, which in turn cools the cell.
The LNCS (shown here) can be autofilled in your laboratory using the DSC touch screen or through the instrument control software. This requires a low pressure 170 kPa gauge maximum (25 psig bulk storage tank to be located within 1.8 m (6 ft) of the LNCS. You can also fill the LNCS at a remote location by disconnecting it from the instrument and moving it to a bulk storage source. The LNCS fill/reset button is used for the autofill function or the tank can be manually filled.